 Challenges of Rural Marketing
Challenges of Rural Marketing
According to the World Bank Open Data, about 44% of the world’s population currently lives in rural areas. Several studies suggest a steady increase in the disposable income and purchasing power of consumers living in rural areas. Rural prosperity creates opportunities for domestic and multinational companies to maximize revenue and profit by implementing rural marketing strategies. Many companies already leverage rural marketing by planning and launching various rural-specific products and services. They boost the demand for products/services in rural markets by focusing on distribution, pricing, and promotion. However, many companies and startups still find it challenging to enter into rural markets and capture rural market share. Understanding these rural marketing problems is crucial for businesses to develop effective strategies and tap into the rural economy successfully. Some of these challenges of rural marketing emerge when rural marketers fail to understand the specific and distinct characteristics of rural markets. At the same time, they have to manage several rural marketing challenges due to the preferences and expectations that differentiate rural consumers from urban consumers.
Hence, a company has to address a slew of challenges while implementing rural marketing concepts like urban to rural, rural to urban, and rural to rural. We can identify and understand some of these major challenges of rural marketing based on information gathered from diverse sources.
What is Rural Marketing?
Rural marketing refers to the process of promoting and selling products and services in rural areas, where the population resides outside urban centers. It involves understanding the unique needs, behaviors, and preferences of rural consumers and tailoring marketing strategies accordingly. Unlike urban marketing, rural marketing demands more localized, culturally sensitive, and cost-effective approaches due to factors like lower literacy rates, limited digital access, and strong community influence. It encompasses both agricultural and non-agricultural products that are marketed to rural consumers. With a large percentage of the population still living in rural regions in countries like India, rural marketing plays a crucial role in driving national economic growth. As infrastructure and digital connectivity improve, this segment offers immense untapped potential for brands.
Importance of Rural Marketing
Rural marketing is important because it targets a vast and growing segment of the population that contributes significantly to the economy. Rural consumers are increasingly aspiring for quality products and better lifestyles, thanks to rising incomes and exposure to media. Brands that successfully engage with rural markets can benefit from increased sales volume and long-term customer loyalty. Moreover, rural marketing also helps in the equitable distribution of goods and services across the country. It promotes inclusivity, bridges the urban-rural divide, and supports local economies. For businesses, tapping into rural demand is no longer optional—it’s a strategic imperative.
Key Aspects of Rural Marketing
Rural marketing involves several unique characteristics that differentiate it from urban-focused strategies. These include understanding rural buying behavior, which is often influenced by community leaders, traditions, and festivals. Pricing sensitivity is another key factor, as consumers usually have irregular incomes tied to agricultural cycles. Distribution can be challenging due to underdeveloped infrastructure, making last-mile delivery and rural intermediaries critical. Additionally, communication strategies need to be highly localized—using regional languages, visual messaging, and culturally relevant storytelling. Brands must also invest in building trust and relationships, as rural consumers value credibility over flashy promotions.
Understanding Major Problems and Challenges of Rural Marketing
Let’s explore the major challenges of rural marketing in India, supported by real-world examples.
1. Income Inequality
Several studies suggest a consistent increase in agricultural income. Also, many people living in rural areas these days earn recurring income by engaging in non-agricultural activities. However, the data released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) suggests that over 63% of people experiencing poverty live in rural areas. Income inequality and rural poverty reduce the purchasing power of a significant percentage of rural consumers.
Example:
Amul’s dairy cooperative model has helped bridge the income inequality gap by enabling small farmers and dairy producers to earn steady incomes, empowering rural communities economically.
2. Poor Infrastructure
One of the most significant challenges in rural marketing is the lack of proper infrastructure. Many rural areas still suffer from poor roads, inadequate transportation, and limited storage facilities, making the distribution of goods difficult. Poor connectivity leads to high costs in logistics and supply chain inefficiencies, resulting in higher prices for consumers and lower profit margins for businesses.
Example:
Companies like Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL) have tackled this challenge by leveraging low-cost distribution models. HUL’s “Project Shakti” trains local women to become micro-entrepreneurs, ensuring that products reach even the remotest villages where traditional supply chains fail.
3. Low Literacy Levels
A large portion of the rural population has lower literacy rates compared to urban consumers. This affects marketing communication, as traditional advertising methods such as newspapers, online ads, and written instructions may not be effective. Brands must rely on visual and audio-based communication, such as radio, television, and pictorial packaging, to reach rural consumers effectively.
Example:
Colgate tackled this issue by running oral hygiene awareness programs using street plays and interactive sessions in local languages, ensuring rural consumers understood the importance of their products without relying on text-heavy advertisements.
4. Uneven Population Spread
Major rural markets in a country consist of hundreds of villages. However, the size of the consumer base varies across rural markets. Likewise, the purchasing power of consumers varies across rural markets. That is why companies find it challenging to boost a product’s availability and affordability simultaneously in various rural markets. Also, they have to implement multiple marketing and promotional strategies to target consumers living in specific rural markets.
Example:
FMCG companies like Dabur and HUL have adopted cluster-based marketing strategies, where they focus on select villages at a time rather than targeting all rural areas simultaneously. This helps optimize logistics and marketing efforts efficiently.
5. Language Diversity
While creating marketing content and ads for urban consumers, companies prioritize English over local languages. However, a significant percentage of consumers living in rural areas are not proficient in English. Companies can attract, engage, and influence rural consumers only by communicating in their native language. Language diversity creates communication barriers that make it challenging for enterprises to introduce and promote their offerings in rural markets.
Example:
Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea localized their advertisements and customer support services by offering multilingual helplines and promotions in regional languages, ensuring better engagement with rural customers.
6. Price Sensitivity and Low Purchasing Power
Rural consumers are highly price-sensitive due to lower disposable incomes. They tend to prioritize essential goods over luxury or premium products. Brands must consider affordability while designing their products and pricing strategies to ensure they align with the financial realities of rural consumers.
While making rural marketing strategies, companies have to focus on keeping products or services affordable. Some enterprises offer products at lower rates, while others launch rural-specific product editions. The differential pricing makes it challenging for enterprises to determine break-even pricing. They can recover costs only by selling a larger number of products in rural markets.
Example:
To counter this, PepsiCo introduced smaller, more affordable SKUs (Stock Keeping Units) like ₹5 packs of Kurkure and Lay’s, making their products accessible to price-conscious rural consumers.
7. Limited Retail and Distribution Channels
Large consumer goods and FMCG companies have already set up robust distribution systems across rural markets. However, small companies and startups lack the resources and network required to make products available across rural markets. The low sales volume makes it challenging for them to open stores or outlets in various rural markets. Also, they find it difficult to find reliable retailers who will manage marketing and sales in rural markets.
The rural retail landscape is highly fragmented and dominated by small, local shops (kirana stores) and informal markets. Unlike urban areas where organized retail chains exist, rural consumers depend on small vendors, which leads to inefficiencies in product availability and pricing. Companies must invest in building strong distribution networks and partnerships with local retailers to improve accessibility.
Unlike urban markets with well-established retail chains, rural India relies heavily on small Kirana stores, haats (weekly markets), and panchayat-led cooperatives. Ensuring product availability across these fragmented retail points is a major challenge.
Example:
Coca-Cola India adopted the “Hub and Spoke” distribution model, wherein products are stocked in larger rural towns and transported to nearby villages through local distributors. This helped them maintain a consistent supply chain in rural areas.
8. Lack of Infrastructural Facilities
Companies find it easier to launch and market products in urban markets due to robust infrastructure. Poor infrastructural facilities make it challenging for them to market existing products and launch new products in rural markets. Many companies overcome this challenge using conventional distribution channels. However, they still find it difficult to ensure product availability due to the absence of proper transportation and road connectivity.
Example:
Maruti Suzuki struggled with vehicle distribution in remote villages due to poor road conditions. To overcome this, the company introduced mobile showrooms—vehicles fitted with demo models and sales representatives—to reach potential buyers in areas with poor infrastructure.
9. Cultural and Regional Diversity
India’s rural market is not homogeneous; it consists of diverse languages, traditions, and cultural preferences. A marketing strategy that works in one region may not work in another. Businesses must adapt their branding, packaging, and promotional campaigns to cater to local tastes and preferences to establish a strong connection with rural consumers.
Example:
ITC’s e-Choupal initiative provides customized agricultural solutions to farmers based on local climatic conditions and crop requirements. This personalized approach helps in building trust among rural consumers.
10. Demand Fluctuations
Despite new employment opportunities, a large percentage of rural people rely on agriculture. Their purchasing power increases after copping seasons. However, farming seasons vary across rural areas. Hence, agriculture makes rural markets seasonal. Also, many consumers lack the purchasing power required to avail of high-value products and services. Companies find it challenging to boost the sale of non-consumer durables in rural markets throughout the year.
Example:
Bajaj Auto strategically times its motorcycle launches and financing schemes around harvest seasons when farmers have more disposable income.
11. Warehouse Quality Control
Rural areas and markets differ from each other in the category of road connectivity and density. Many villages are still not connected with rural areas. Companies overcome transportation challenges using warehousing. However, most warehouses in developing countries are located in urban and suburban areas. Also, the warehouses located in rural areas are not managed and controlled by organized agencies.
Example:
The Food Corporation of India (FCI) has faced significant challenges in maintaining proper warehousing infrastructure in rural areas, leading to food grain spoilage and wastage. To address this, private players like Adani Agri Logistics have developed modern silos and cold storage facilities to enhance quality control and reduce post-harvest losses.
12. Seasonal Demand Fluctuations and Market Unpredictability
Rural incomes are often dependent on agriculture, making them highly seasonal. Purchasing power rises during harvest seasons and drops during off-seasons. This cyclic nature of demand requires businesses to plan their marketing and sales efforts strategically, offering discounts, credit facilities, or special schemes during off-peak periods to maintain steady sales.
Unlike urban markets, rural markets are uncertain and unpredictable. Marketers find it challenging to understand and predict rural consumer behavior due to a lack of reliable data. Hence, they implement commonly used urban marketing strategies. However, the inability to make data-driven decisions makes it difficult for them to customize and update marketing tactics according to recent changes and emerging trends. The market unpredictability often discourages companies from entering new rural markets.
Example:
Hero MotoCorp faced challenges predicting rural demand but overcame this by closely monitoring festival seasons, harvest cycles, and monsoon patterns to time their product launches and financing schemes effectively.
13. Lack of Market Research and Consumer Insights
Due to the complexity and vastness of rural markets, gathering reliable data on consumer behavior, purchasing habits, and preferences is challenging. The lack of structured market research leads to ineffective marketing strategies. Companies must invest in on-ground surveys, local partnerships, and AI-driven data collection techniques to gain deeper insights into rural consumers.
Example:
Nestlé India used on-ground research teams and direct consumer interactions to understand rural eating habits, leading to the successful adaptation of Maggi flavors to match regional tastes.
14. Lack of Trust in Brands
Rural consumers are cautious about adopting new brands and often rely on word-of-mouth recommendations and community influence before making purchase decisions.
Example:
Patanjali successfully built trust in rural markets by aligning its brand with Ayurveda, a concept deeply rooted in Indian tradition. The endorsement of Baba Ramdev also helped in building credibility among rural consumers.
15. Unconventional Media Consumption
Rural consumers do not engage with mainstream media the same way urban consumers do. While television and radio are popular, digital penetration remains low in many areas.
Example:
Mahindra & Mahindra leveraged folk music and local theater to promote its tractors and farm equipment in rural fairs (melas), effectively reaching farmers in their native settings.
16. Cash-Driven Economy and Digital Payment Barriers
Despite a rise in digital transactions post-demonetization and UPI growth, cash remains the primary mode of transaction in rural areas. Limited access to banking services and internet connectivity hinders digital payments.
Example:
Paytm and PhonePe launched extensive offline marketing campaigns to educate rural users about digital transactions, often employing local influencers to demonstrate how these payment systems work in local Kirana stores.
Solutions to Rural Marketing Problems
Despite these challenges, businesses can overcome rural marketing obstacles by adopting new innovations in rural marketing and localized strategies:
Improving Supply Chains: Companies can partner with local distributors, invest in rural logistics, and leverage government infrastructure projects to streamline distribution.
Localized and Visual Advertising: Using vernacular languages, regional branding, and pictorial representations can make marketing campaigns more effective.
Digital and Mobile Outreach: Expanding access to digital tools such as mobile banking, WhatsApp-based commerce, and digital kiosks can bridge the technology gap.
Affordable Pricing Strategies: Offering smaller package sizes, sachets, and budget-friendly variants can help attract rural consumers.
Community Engagement and Trust Building: Conducting product demonstrations, sponsoring local events, and using rural influencers can enhance brand credibility.
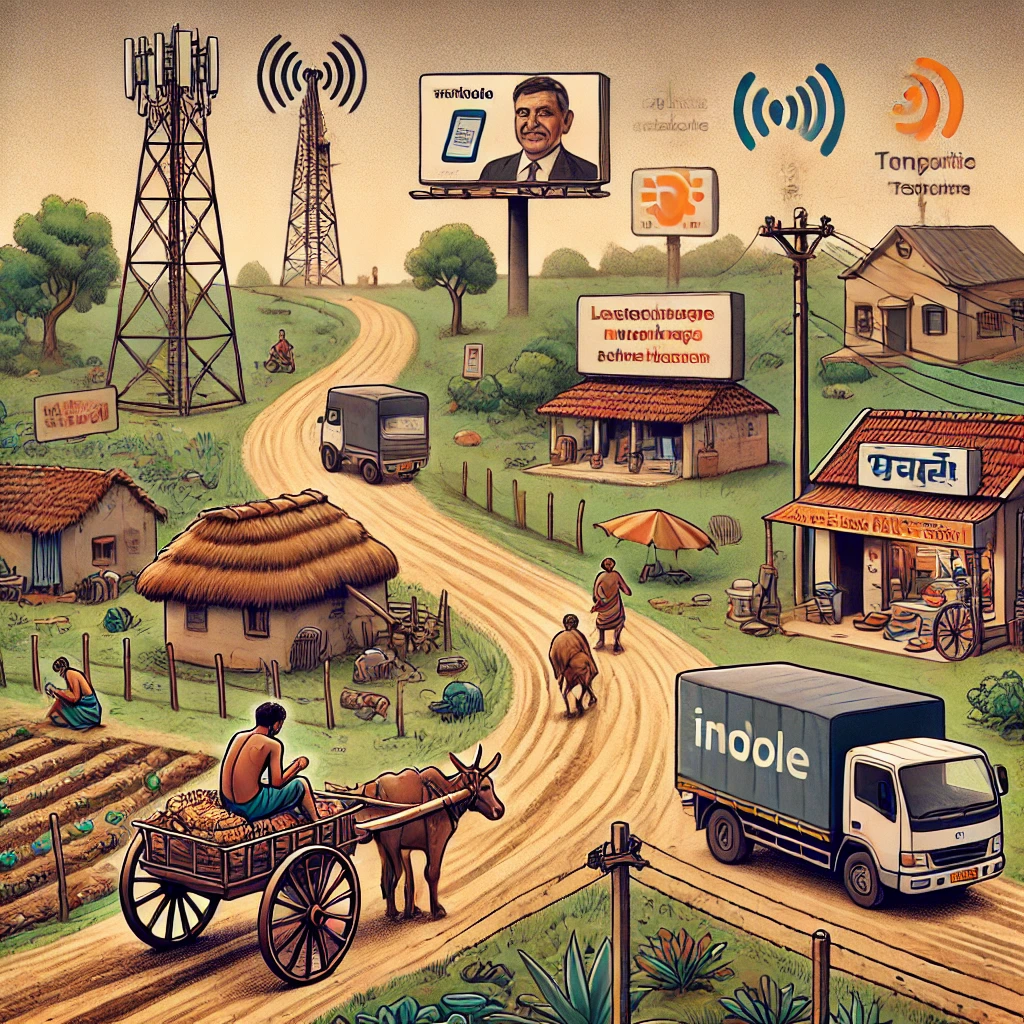

Conclusion
Rural marketing creates opportunities for enterprises to maximize revenue by leveraging the number and purchasing power of consumers living in rural areas. However, no company can enter into rural markets and gain market share without overcoming several problems and challenges of rural marketing. The rural marketing challenges vary across regions.
In some countries, governments have been extending the scope of rural marketing by prioritizing and accelerating rural infrastructure development. Likewise, per capita income, level of literacy, and communication facilities vary across rural areas. That is why companies must customize rural marketing strategies to address and overcome rural marketing challenges faced in each targeted rural market.
This is the third blog in this blog series on Rural Marketing. The other blogs in this series are types of rural marketing and rural marketing in India.








Leave a Reply